- The sectoral contribution to the GDP growth significantly declined, with transport and storage only posting a paltry growth.
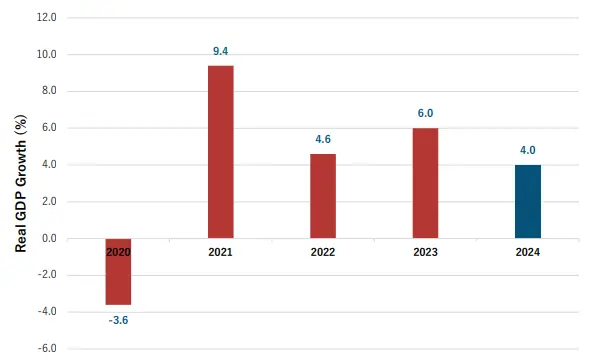
- The GDP grew by 4.0% compared to 6.0% of the corresponding quarter of 2023.
- There was an ease of inflationary pressure during the quarter under review compared to a similar quarter in 2023.
A statistical report by the Kenya National Bureau of Statistics (KNBS) on Kenya’s GDP report in the third quarter of 2024 shows decelerated growth compared to the respective quarter of 2023.
“Kenya’s economy grew by 4.0 per cent in the third quarter of 2024 compared to 6.0
per cent growth in the corresponding quarter of 2023. The decelerated growth was
largely due to a general decline in growth in most sectors of the economy,” KNBS reported.
The GDP growth in the 3rd quarter of 2023 was however slightly higher compared to the corresponding quarter of 2022, when the economy contracted to 4.6 percent.
The report shows that Kenya recorded the worst GDP decline in the last four years in 2020, when the economy constricted to -3.6 percent in Q3, possibly due to Covid-19 pandemic shocks. However, there was an uptick in growth, the highest in the last four years, when the economy accelrated to 9.4 percent in 2021.
The quarter under review shows a downward trend, with the GDP declining by 2.0 percent from 6.0 percent in 2023 to 4.0 percent in 2024. KNBS attributes the paltry growth to a section of sectors of the economy, especially in the construction and mining and quarrying activities.
Sectoral Contribution to the GDP Growth Analysis
The report shows that the construction activities declined by 2.0 percent, while mining and quarrying recorded a decline of 11.1 percent in the third quarter of 2024.
“The growth was constrained by contractions in Construction and Mining and Quarrying
activities. Construction activities contracted by 2.0 per cent while Mining and
Quarrying posted a contraction of 11.1 percent in the quarter under review.”
The growth, however, received a huge boost from agricultural, forestry, fishing, transportation and storage, financial and insurance, real estate, wholesale retail, accommodations, and food service activities.
Agriculture, forestry, and fishing contributed 4.2 percent to the economy. Transport and storage activities posted a growth of 5.2%, while financial and insurance activities contributed 4.7%. Real estate and whole and retail activities recorded growth of 5.5% and 4.8%, respectively. However, accommodations and food services posted the highest growth, contributing 13.7% to the economy.
There was a slight decrease in inflationary pressure, according to the report, in the quarter under review, driven by lower prices of food and non-alcoholic beverages. The quarter recorded an average ease of inflation of 4.08% from 6.93% in the corresponding quarter of 2023.
Additionally, the Kenyan shilling appreciated against all major currencies in the third quarter of 2024 compared to the preceding quarter of 2023. The shilling appreciated against the US Dollar, EURO, and Starling Pund by 10.1%, 9.3%, and 7.7%, respectively.
The Kenya Shilling also gained a strong ground against the regional currencies, the Tanzanian shilling and Uganda shilling, by 21.2% and 11.7%, respectively. There was, however, a sharp decline against the Japanese Yen and the South African Rand: 12.7% and 6.7%, respectively.
The quarter under review also saw the Central Bank Rate (CBR) reviewed downwards to 12.75% in both August and September, from 13.00% in July 2024, compared to 10.50% for the corresponding months of 2023.
The Nairobi Security Exchange (NSE) 20 Share Index grew by 17.8% to 1,775.7 points in September 2024 from 1,508.0 in the similarly month of 2023. The Borad money supply (M3) rose from Ksh 5,841.1 billion as at the end of September 2023 to 5,992.1 billion as at the end of September 2024